Sponsored
Blood Glucose Monitoring: Understanding Your Blood Sugar Levels Through Regular Monitoring

What is Blood Glucose Monitoring?
Continuous glucose monitor, also known as blood sugar monitoring, refers to checking the level of glucose or sugar in one's blood. Glucose is the main source of energy for our cells and blood glucose levels need to be kept within a narrow range for the body to function properly. Continuous glucose monitor helps people, especially those with diabetes, keep track of how well their blood sugar levels are controlled. It provides valuable information to both patients and healthcare providers regarding any adjustments needed in lifestyle, medications or treatment plans.
Devices Used For Blood Glucose Monitoring
The most common devices used for continuous Blood Glucose Monitoring are glucose meters and test strips. A glucose meter is a small portable electronic device that reads the glucose level from a small drop of blood, typically obtained via a finger prick. Test strips are disposable, single-use strips that are inserted into the meter. As the blood sample is applied to the test strip, the meter analyzes the blood glucose concentration using an electrochemical reaction and displays the result in either milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Most glucose meters give results within 5 seconds. Some advanced meters can also store past test results and transmit data to apps or computers for easier tracking.
Factors Affecting Blood Glucose Levels
There are many factors that can cause fluctuations in a person's blood glucose levels throughout the day. Some of the key factors include:
- Meal timing and content: Carbohydrate intake from meals and snacks is a major influence on post-meal blood glucose levels. Higher carb foods lead to greater rises.
- Medications: Oral diabetes medications, insulin doses and other drug therapies can impact blood sugar levels. Adjustments may be needed due to side effects or changes in other factors.
- Illness and stress: Physical illness, infections, emotional stress etc. can increase blood glucose due to release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
- Exercise: Physical activity generally lowers blood sugar but it may rise initially depending on intensity and timing relative to food intake.
- Hormonal changes: Growth hormone, cortisol and other hormonal fluctuations can temporarily raise or lower glucose levels at different times of the day.
- Alcohol intake: Alcohol prevents the liver from releasing stored glucose, causing levels to initially drop. A rebound high may occur later once alcohol is metabolized.
- Sleep patterns: Blood glucose levels tend to dip lower during sleep and rise in the early morning hours. This dawn phenomenon needs to be accounted for.
Get More Insights on- Blood Glucose Monitoring
Categories
Read More
According to the Regional Research Reports, the global air freight service market size is projected to be a million USD in 2022 to multi-million USD in 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 10.2% from 2023 to 2033. Regional Research Reports Insights has recently released a new report titled "Air Freight Service 2023" which presents valuable regional and global...

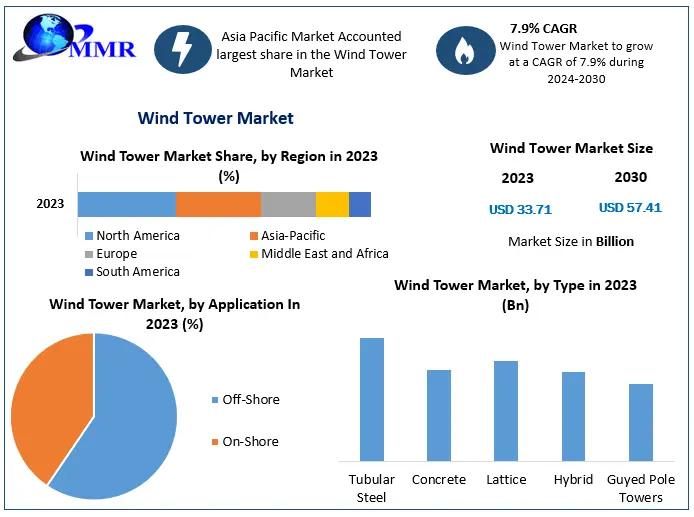
Wind Tower Market Overview: Maximize Market Research, a Wind Tower business research firm has published a report on the “Wind Tower Market”. Which provides Industry Analysis (Market Performance, Segments, Price Analysis, and Outlook). Estimated Growth Rate for Wind Tower Market: Global Wind Tower Market size was valued at USD 68.59 Bn in 2023 and is expected to reach USD...