Software-Defined Networking Market Key Players Analysis, Opportunities
Software-Defined Networking 2024
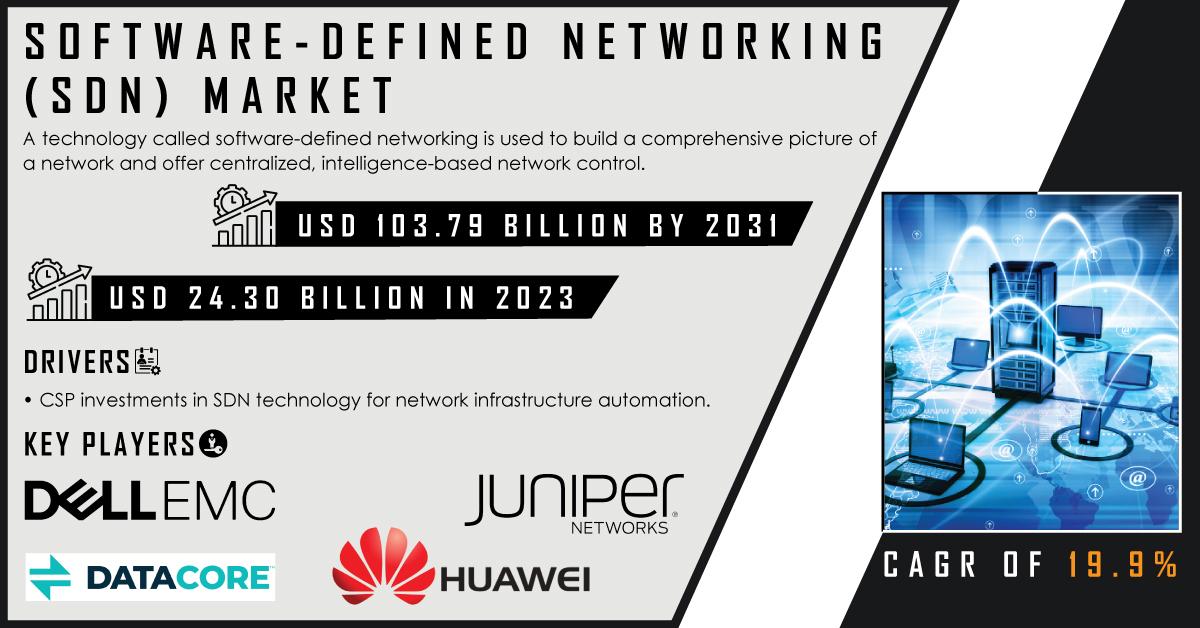
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, the demand for efficient and scalable networking solutions has never been more critical. As organizations expand their IT infrastructure to accommodate growing data traffic, traditional networking methods often struggle to keep pace with the requirements of modern businesses. Enter Software-Defined Networking (SDN), a revolutionary approach that decouples network control from the physical hardware, providing enhanced flexibility, scalability, and automation. The growing interest in SDN is reflected in the Software-Defined Networking Market Share, which was valued at USD 24.30 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 124.4 billion by 2032, growing at a remarkable CAGR of 19.9% over the forecast period from 2024 to 2032.
At its core, SDN represents a fundamental shift in how networks are designed, operated, and managed. Traditional networking relies heavily on hardware-based devices, where each component, such as routers and switches, operates independently with limited visibility into the overall network. In contrast, SDN centralizes control in a software-based management system, allowing for more efficient allocation of resources and improved visibility across the entire network.
Key Components of Software-Defined Networking
SDN architecture consists of three primary components: the application layer, the control layer, and the data layer. The application layer encompasses the network applications and services that utilize the network's capabilities, enabling functions such as network analytics, security management, and service orchestration. This layer is responsible for providing a user-friendly interface for administrators to interact with the network and define policies and requirements.
The control layer is the heart of SDN, serving as the centralized brain that manages the network's operation. It consists of a software controller that communicates with both the application layer and the data layer. The controller enables administrators to programmatically manage and configure network resources, making it easier to adapt to changing demands and troubleshoot issues.
The data layer includes the physical hardware devices that comprise the network, such as switches, routers, and other network appliances. Unlike traditional networks, where these devices perform both control and data forwarding functions, in SDN, they operate as simple forwarding devices. This separation allows for greater agility, as changes can be made in the control layer without requiring physical modifications to the hardware.
Benefits of Software-Defined Networking
The transition to SDN offers numerous benefits for organizations seeking to optimize their network infrastructure. One of the most significant advantages is increased agility. With traditional networking, deploying new services or adjusting network configurations often requires substantial time and effort. SDN simplifies these processes by allowing administrators to make changes programmatically through a centralized controller. This capability enables organizations to respond rapidly to changing business needs, reducing the time to market for new applications and services.
Another critical benefit is enhanced scalability. As businesses grow, so too do their networking requirements. Traditional hardware-based solutions can be limited by the physical constraints of devices, making it challenging to scale efficiently. SDN, on the other hand, enables organizations to add new devices and services seamlessly, allowing them to scale their networks according to demand without significant disruption.
Moreover, SDN enhances network visibility and control. The centralized nature of SDN allows administrators to gain real-time insights into network performance, traffic patterns, and security events. This visibility facilitates proactive management, enabling organizations to identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
Security is another area where SDN provides advantages. Traditional networks often suffer from vulnerabilities arising from complex configurations and multiple hardware components. SDN simplifies security management by enabling organizations to enforce policies consistently across the entire network from a centralized point. Additionally, the programmable nature of SDN allows for the rapid deployment of security measures in response to emerging threats.
Cost reduction is also a notable benefit of adopting SDN. By reducing reliance on proprietary hardware and facilitating more efficient resource utilization, organizations can achieve significant cost savings over time. The ability to automate network management tasks further decreases operational expenses, allowing IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine maintenance.
Challenges in Implementing Software-Defined Networking
Despite its numerous advantages, the implementation of SDN is not without challenges. One of the primary hurdles organizations face is the need for a cultural shift within their IT teams. The move to SDN requires a change in mindset, as traditional networking skills may not fully translate to the new paradigm. Organizations must invest in training and development to equip their teams with the knowledge and skills needed to manage and operate SDN effectively.
Interoperability is another concern. Many organizations operate within heterogeneous environments, utilizing a mix of legacy systems and modern technologies. Ensuring that SDN solutions can integrate seamlessly with existing infrastructure is critical for successful implementation. Organizations must carefully evaluate potential vendors and solutions to ensure compatibility with their current systems.
Moreover, the security implications of SDN must be carefully considered. While SDN can enhance security through centralized control, it also introduces new risks. The centralized controller becomes a potential single point of failure, and if compromised, it could jeopardize the entire network. Organizations must implement robust security measures to protect the controller and ensure that security policies are enforced consistently across all layers of the network.
The Future of Software-Defined Networking
The future of SDN looks promising, driven by ongoing advancements in technology and the growing demand for flexible and efficient networking solutions. As organizations continue to adopt cloud computing, IoT, and big data analytics, the need for agile and scalable networks will only increase. SDN is well-positioned to meet these demands, offering the necessary flexibility to accommodate the complexities of modern IT environments.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are expected to play a significant role in shaping the future of SDN. By integrating AI-driven analytics with SDN, organizations can gain deeper insights into network behavior, enabling proactive management and optimization. Additionally, AI can enhance security by automatically detecting and responding to anomalies and threats in real time.
The rise of multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments also presents new opportunities for SDN. As organizations leverage multiple cloud providers to meet their needs, SDN can facilitate seamless connectivity and management across diverse environments. This capability will be critical for organizations seeking to optimize their cloud strategies and improve overall operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Software-Defined Networking represents a significant advancement in network management, providing organizations with the agility, scalability, and control required to thrive in today's fast-paced digital landscape. The growing Software-Defined Networking Market indicates a strong shift toward this innovative approach as businesses recognize the value of centralized control and automation.
As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of modern IT, the benefits of SDN—ranging from cost savings to enhanced security—will play a crucial role in shaping their networking strategies. By embracing SDN, organizations can position themselves for success in an increasingly interconnected world, ensuring that they remain competitive and resilient in the face of evolving challenges. The future of networking is here, and it is defined by software.
Contact Us:
Akash Anand – Head of Business Development & Strategy
info@snsinsider.com
Phone: +1-415-230-0044 (US) | +91-7798602273 (IND)
About Us
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Read Our Other Reports:
- Software-Defined_Networking_Market
- Software-Defined_Networking_Market_Size
- Software-Defined_Networking_Market_Share
- Software-Defined_Networking_Market_Growth
- Software-Defined_Networking_Market_Trends
- Software-Defined_Networking_Market_Report
- Software-Defined_Networking_Market_Analysis
- Software-Defined_Networking_Market_Forecast
- Software-Defined_Networking_Industry
- Software-Defined_Networking_Market_Research
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- الألعاب
- Gardening
- Health
- الرئيسية
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- أخرى
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


