What Tests Are Used to Diagnose Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, Why Accurate Testing is Essential, and How to Prepare for Your Appointment

Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) is a complex condition that occurs when the nerves, blood vessels, or both are compressed in the space between your collarbone and first rib, known as the thoracic outlet. Given the variety of symptoms associated with TOS and its similarity to other conditions, diagnosing TOS can be challenging. Accurate testing is essential for identifying the type and severity of the syndrome to ensure proper treatment. In this article, we will explore the different tests used to diagnose Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, why precise testing is crucial, and how you can prepare for your appointment to ensure the best outcome.
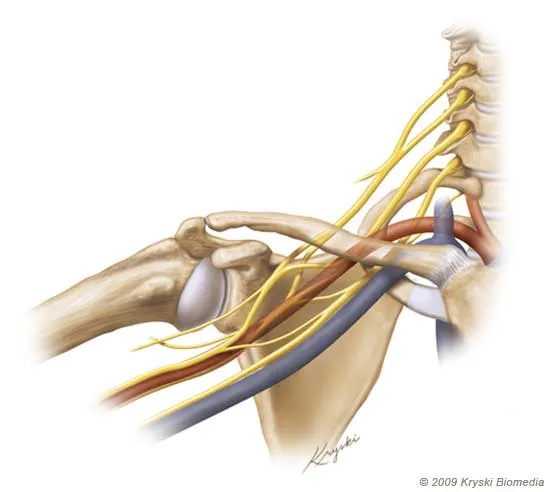
Understanding Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome is categorized into three types, depending on the structure that is compressed:
Neurogenic TOS: Involves compression of the brachial plexus, the network of nerves that control muscle movements and sensations in the shoulder, arm, and hand.
Venous TOS: Occurs when veins are compressed, affecting blood flow from the arms to the heart, which can result in swelling and clot formation.
Arterial TOS: The rarest form of TOS, caused by compression of the arteries, which affects blood flow to the arms and hands.
Each type of TOS presents distinct symptoms, requiring different diagnostic approaches to pinpoint the cause of compression.
Why Accurate Testing is Essential
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome often presents symptoms that can overlap with other conditions, such as cervical spine disorders, carpal tunnel syndrome, and rotator cuff injuries. This overlap makes it difficult to diagnose TOS based on symptoms alone. For instance, numbness and tingling in the hands can be mistaken for a nerve disorder unrelated to TOS. Without proper testing, a misdiagnosis is possible, leading to ineffective treatment and prolonged discomfort.
Accurate diagnostic testing helps:
Identify the type of TOS: Determining whether the condition is neurogenic, venous, or arterial is crucial for selecting the correct treatment approach.
Assess the severity of compression: Imaging and functional tests provide insight into how severe the compression is and which structures are affected.
Rule out other conditions: Testing helps differentiate TOS from other disorders that might present similar symptoms.
Tailor the treatment plan: With a clear diagnosis, healthcare providers can develop a treatment strategy that may include physical therapy, medication, or surgery.
What Tests Are Used to Diagnose Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
The diagnosis of TOS typically involves a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests, and other diagnostic procedures. Here are the most common tests used to confirm the presence of TOS:
1. Physical Examination and Provocative Tests
A thorough physical exam is often the first step in diagnosing TOS. During the exam, your doctor will evaluate your posture, range of motion, and areas of tenderness. They may also perform provocative tests, which are designed to reproduce the symptoms of TOS by putting the thoracic outlet structures under stress. Some common provocative tests include:
Adson’s Test: You will be asked to take a deep breath and turn your head while the doctor checks for a reduction in the pulse in your arm. A decreased pulse may indicate arterial compression.
Roos Test (Elevated Arm Stress Test): In this test, you will raise your arms to shoulder height and open and close your hands for several minutes. The onset of symptoms such as pain, numbness, or tingling can suggest neurogenic TOS.
Wright’s Test: The doctor will raise your arm and check your pulse, particularly focusing on whether symptoms like numbness or a weakened pulse occur.
While these tests are useful in raising suspicion of TOS, they are not definitive. Additional imaging and diagnostic procedures are needed for a more accurate diagnosis.
2. Imaging Tests
Imaging studies are critical for visualizing the structures around the thoracic outlet and determining the cause of compression.
X-rays: X-rays are often the first imaging test performed to rule out bony abnormalities, such as an extra rib (cervical rib) or abnormal bone structure in the shoulder or neck. These findings may help confirm a diagnosis of TOS.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI provides a more detailed view of the soft tissues, nerves, and blood vessels in the thoracic outlet. This test is especially useful for detecting neurogenic TOS, as it can show nerve compression and any abnormalities in the brachial plexus.
CT Scan (Computed Tomography) with Contrast: A CT scan with contrast dye is typically used to assess arterial and venous TOS. It provides detailed images of the blood vessels and helps identify areas of vascular compression or blockage. A CT angiogram may be ordered to evaluate blood flow and identify any clots or narrowing of the vessels.
3. Electrodiagnostic Testing
For patients with suspected neurogenic TOS, electrodiagnostic tests can be valuable in confirming nerve compression. These tests measure the electrical activity in the muscles and nerves, providing insight into how well they are functioning.
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): This test measures how fast electrical signals move through your nerves. Slower-than-normal signals may indicate nerve damage or compression consistent with neurogenic TOS.
Electromyography (EMG): An EMG assesses the electrical activity in your muscles when they are at rest and when they are contracting. Abnormal results can indicate nerve damage related to TOS.
4. Vascular Studies
If venous or arterial TOS is suspected, vascular studies can be used to assess blood flow through the veins and arteries in the arms and neck.
Doppler Ultrasound: A Doppler ultrasound uses sound waves to evaluate blood flow in the arteries and veins. It can detect narrowing, clots, or restricted blood flow in the vessels of the thoracic outlet, which is especially useful in diagnosing venous and arterial TOS.
Venography and Arteriography: These tests involve injecting a contrast dye into the veins or arteries and taking X-rays to examine blood flow. They are typically used to diagnose vascular forms of TOS, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or arterial blockages.
5. Posture and Movement Analysis
In some cases, healthcare providers may use posture and movement analysis to evaluate the mechanical causes of TOS. This can involve a detailed examination of how you perform everyday activities, such as lifting or carrying objects, which may contribute to the symptoms.
How to Prepare for Your Appointment
Preparing for your appointment ensures that you get the most accurate diagnosis and treatment recommendations. Here are some tips to help you prepare:
1. Keep a Symptom Journal
Before your appointment, it is helpful to keep a record of your symptoms. Note when the symptoms occur, what activities trigger them, and how long they last. Be specific about the location and nature of the pain or discomfort (e.g., “numbness in the fingers after holding my arms overhead”). This will help your doctor understand the severity and patterns of your symptoms.
2. Bring Medical Records and Imaging
If you’ve had previous imaging tests (such as X-rays or MRIs), bring those records to your appointment. These can provide your doctor with a more comprehensive view of your medical history and help rule out other conditions.
3. List of Medications
Make a list of any medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Some medications can affect the symptoms of TOS or interact with treatments.
4. Prepare Questions
It’s important to have a list of questions ready to ask your doctor during your appointment. You might ask:
What type of TOS do you suspect I have?
What tests will confirm the diagnosis?
How can I manage my symptoms while waiting for the test results?
What are the treatment options based on the diagnosis?
5. Wear Comfortable Clothing
You may be asked to perform certain physical movements or provocative tests during your appointment. Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing that allows easy access to your arms, neck, and shoulders for the physical examination.
Conclusion
Diagnosing thoracic outlet syndrome testing requires a careful combination of physical examinations, imaging tests, and functional assessments. Given the complexity of TOS and its similarity to other conditions, accurate testing is essential for determining the type of TOS and guiding effective treatment. By understanding the diagnostic process and preparing for your appointment, you can ensure a smoother, more productive experience with your healthcare provider. If you suspect you have TOS, seek medical attention early to avoid complications and improve your chances of a successful recovery.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness


