Sponsored
A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Architectural Rendering for Modern Design
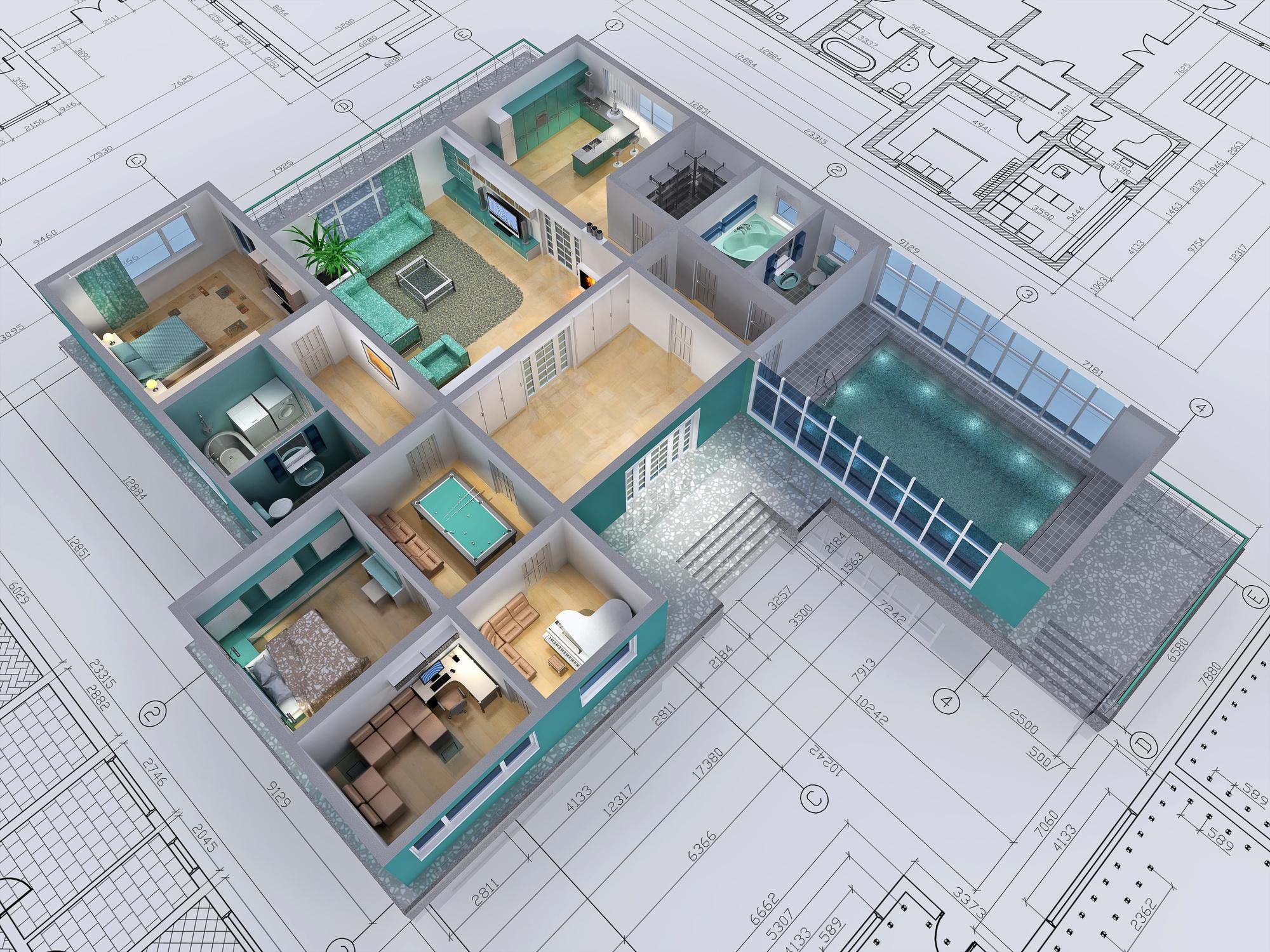
3D architectural rendering has redefined how we envision, design, and communicate architectural projects. By creating detailed, lifelike representations of buildings and spaces before construction even begins, this technology offers architects and clients a new way to visualize ideas. In this article, we’ll dive into what 3D architectural rendering entails, explore the techniques used to create these images, discuss its key advantages, and look toward the future of this ever-evolving field.
What is 3d architectural rendering
At its core, 3D architectural rendering is the process of creating three-dimensional visual representations of architectural designs using specialized software. These renderings can depict both exterior and interior spaces with astonishing realism, making it easier for clients, investors, and architects to visualize the final project. Unlike traditional blueprints or flat sketches, 3D renderings bring depth, texture, and lighting into play, allowing for a more immersive experience.
This technology has become indispensable in architecture because it provides a tangible sense of scale, material, and ambiance. Whether it’s a high-rise commercial building or a cozy residential home, 3D architectural rendering helps everyone involved in the project to better understand the design intent.
Techniques used in 3d architectural rendering
Creating a realistic 3D architectural rendering involves several techniques that work together to produce lifelike visuals. Each step in the process requires a blend of technical skill and artistic flair, ensuring that the final result not only looks great but also accurately reflects the architectural design.
Some of the essential techniques include:
- 3D modeling: This is the first and most crucial step in creating any 3D rendering. Architects use software like SketchUp, AutoCAD, or Revit to build a digital model of the space. The model represents the geometry and layout of the structure, giving a solid foundation for the rendering.
- Material and texture mapping: Once the model is built, textures and materials are applied to make it look realistic. Whether it’s brick, glass, wood, or metal, these materials give the model its authentic look.
- Lighting and shadows: Proper lighting is critical for making 3D renderings look realistic. Whether simulating natural sunlight or indoor artificial lighting, getting the shadows and reflections right is key to achieving a photorealistic result.
- Post-production: After rendering, many artists use post-production software like Photoshop to fine-tune the image, adjusting colors, adding environmental details, or enhancing certain elements for a polished look.
By combining these techniques, 3D architectural rendering artists create visuals that not only capture the design but also evoke the desired atmosphere of the project.
Advantages of using 3d architectural rendering
The benefits of 3D architectural rendering go far beyond simple aesthetics. One of the most significant advantages is that it helps architects and clients make better decisions early in the design process. With a clear visual representation, clients can see how materials, lighting, and layouts work together, allowing them to provide feedback before construction begins.
Another key benefit is the ability to catch potential design flaws early. By visualizing the project in 3D, architects can identify and address any issues related to space, structure, or materials before they become costly mistakes. This not only saves time but also prevents unnecessary delays and expenses during the construction phase.
Additionally, 3D architectural renderings are a powerful marketing tool. Developers and real estate professionals use these visuals to attract buyers, showcasing properties in their best light. A well-executed 3D rendering can make all the difference in selling a project, offering potential buyers a vivid preview of their future investment.
The future of 3d architectural rendering
As technology continues to advance, the future of 3D architectural rendering looks even more promising. One major trend on the horizon is the integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) into the architectural rendering process. These tools allow clients to not only view but experience their project in a fully immersive environment. Imagine walking through a virtual model of a home, adjusting the layout or lighting in real-time—that’s the direction architectural rendering is headed.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is also starting to play a role in 3D architectural rendering. With AI, certain aspects of the rendering process can be automated, making it faster and more efficient. Additionally, AI can assist in creating more detailed and accurate simulations, further enhancing the realism of the final product.
The combination of these technologies is pushing 3D architectural rendering to new heights, making it an indispensable tool for anyone in the architecture and design industries. Staying informed about these advancements will ensure that architects and developers continue to deliver cutting-edge designs to their clients.
Conclusion
3D architectural rendering is more than just a design tool—it’s a way to bring ideas to life in a tangible, visual format. From showcasing materials and lighting to catching potential design issues, this technology offers a wealth of benefits for architects, clients, and developers alike. As new advancements in VR, AR, and AI emerge, the capabilities of 3D architectural rendering will only continue to grow, making it an essential part of modern architectural practices.



