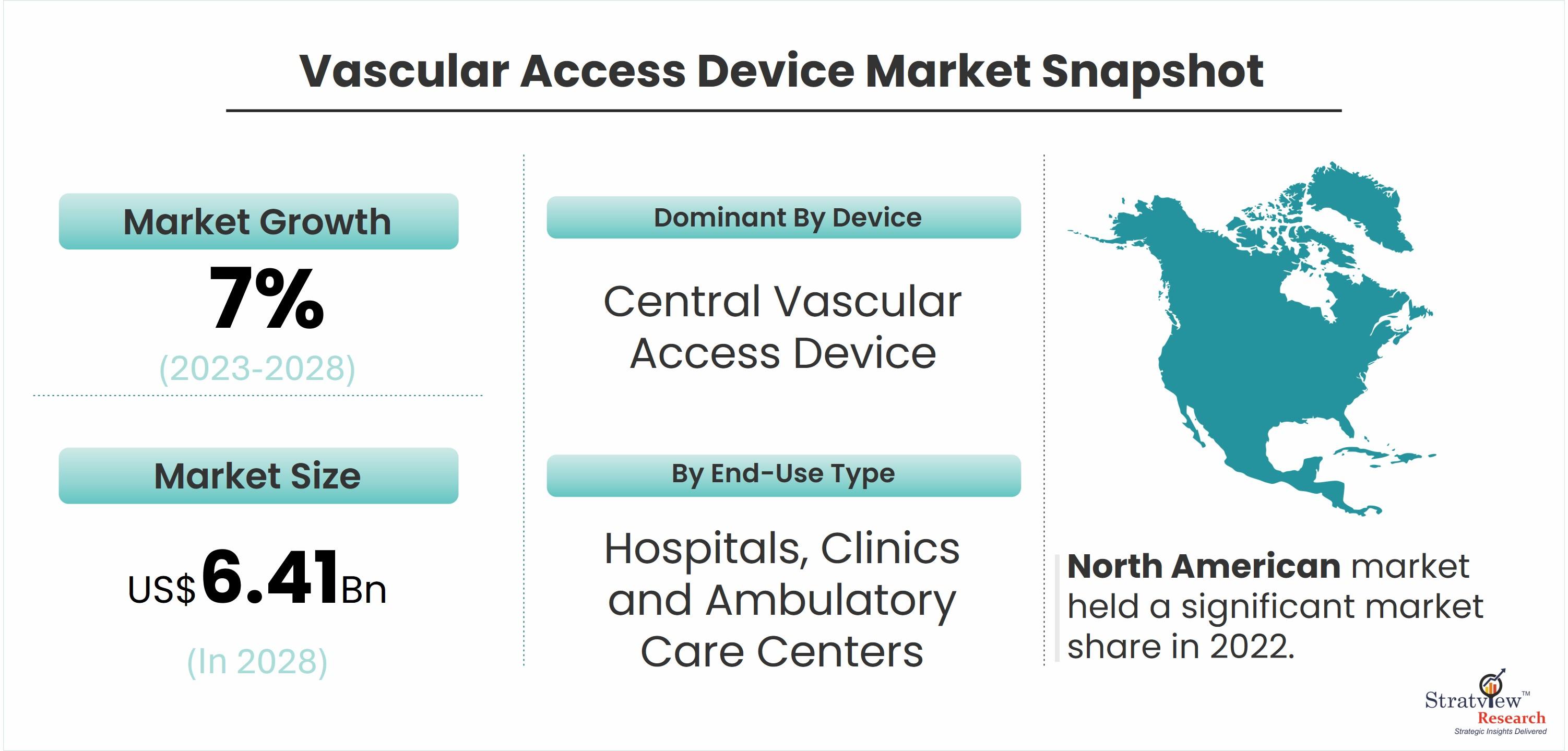
According to Stratview Research, the vascular access device market was valued at USD 4.26 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 7% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 6.41 billion in 2028.
In the intricate realm of healthcare, where precision and efficiency are paramount, the Vascular Access Device Market plays a crucial role in enhancing patient care. As healthcare professionals navigate the complex network of veins to deliver treatments and therapies, the market for vascular access devices continues to evolve, providing insights into advancements that improve patient outcomes. Join us as we delve into the veins of innovation, exploring the dynamics of the Vascular Access Device Market and its impact on the landscape of modern healthcare.
The Importance of Vascular Access:
Vascular access is a critical aspect of medical care, allowing healthcare providers to administer medications, draw blood, and deliver life-saving treatments directly into the bloodstream. Vascular access devices serve as conduits, providing a secure and efficient route to access veins for various medical procedures.
Enhanced Patient Care: The primary goal of vascular access devices is to improve patient care by facilitating essential medical interventions. These devices reduce the need for repeated needle sticks, minimizing patient discomfort and enhancing the overall healthcare experience.
Diverse Applications: Vascular access devices find applications in a broad spectrum of medical situations, from administering chemotherapy and antibiotics to providing parenteral nutrition and monitoring vital parameters. Their versatility makes them indispensable in various healthcare settings.
Types of Vascular Access Devices:
The Vascular Access Device Market offers a range of devices designed to meet specific medical requirements. Understanding these devices is crucial for healthcare professionals to optimize patient care.
Peripheral Intravenous (IV) Catheters: These devices are commonly used for short-term intravenous access. They are inserted into peripheral veins, typically in the arms or hands, and are suitable for a variety of medical treatments.
Central Venous Catheters (CVCs): CVCs are inserted into larger veins near the heart, providing access for a more extended period. They are used for treatments requiring frequent or extended intravenous therapy.
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters (PICCs): PICCs are long, thin tubes inserted into peripheral veins, usually in the arm, and threaded into larger veins near the heart. They offer a less invasive alternative to traditional central venous catheters.
Innovations Driving the Market:
The Vascular Access Device Market is marked by a constant quest for innovation, aiming to enhance safety, efficiency, and patient comfort.
Ultrasound-Guided Insertion: The integration of ultrasound technology has revolutionized the insertion of vascular access devices. Real-time imaging helps healthcare professionals locate veins with precision, reducing the risk of complications.
Antimicrobial Coatings: To minimize the risk of infections associated with catheter use, many devices now feature antimicrobial coatings. These coatings help create a protective barrier, reducing the likelihood of bacterial colonization.
Smart Vascular Access Devices: The advent of smart technology has paved the way for devices that provide real-time data on catheter tip location, blood flow rates, and potential complications. These innovations contribute to safer and more efficient patient care.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While the Vascular Access Device Market continues to advance, it faces challenges such as the risk of infections, thrombosis, and device-related complications. Addressing these challenges opens doors to opportunities for further research, development, and improvement in device design and usage.
Infection Control Measures: Ongoing efforts focus on refining infection control measures, including the development of novel materials and techniques to minimize the risk of infections associated with vascular access devices.
Patient-Centered Designs: Recognizing the importance of patient experience, manufacturers are exploring designs that prioritize patient comfort and minimize the impact of vascular access procedures on daily life.
The Future Landscape:
As we navigate the veins of healthcare, the future of the Vascular Access Device Market holds promise for continued innovation and improvement. Advancements in materials, technology, and procedural techniques are expected to further enhance the safety and efficacy of vascular access.
Conclusion:
In the ever-evolving world of healthcare, the Vascular Access Device Market stands as a testament to the commitment to improving patient care. Navigating veins with precision, innovation, and a focus on patient well-being, the market continues to be a driving force in shaping the future of vascular access. As technology advances and healthcare practices evolve, insights into the dynamics of this market illuminate a path towards a more efficient, safer, and patient-centered approach to vascular access in modern medicine.