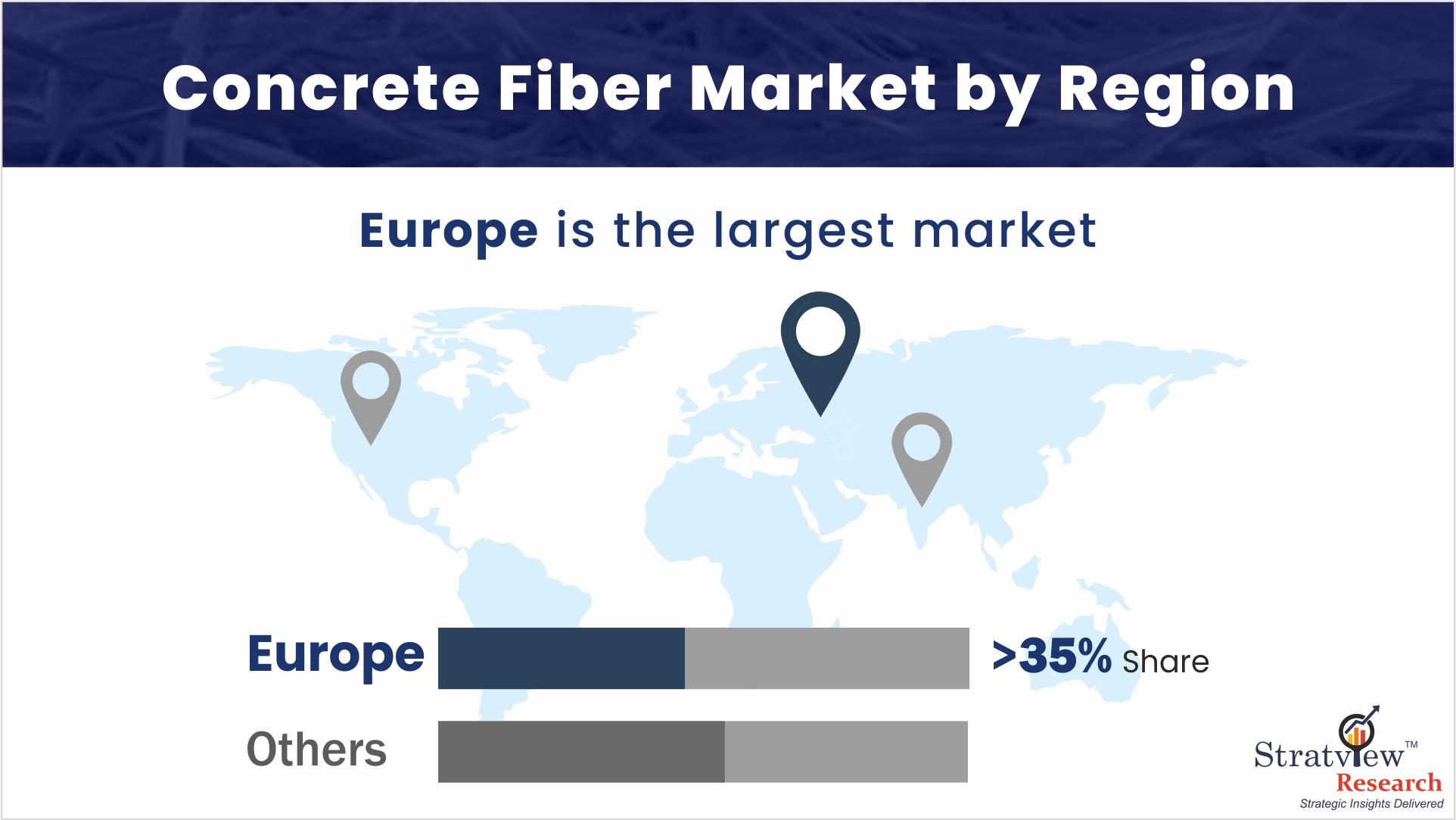
According to Stratview Research, the concrete fiber market was estimated at US$ 1.31 billion in 2021 and is expected to exhibit a healthy CAGR of 5.0% over the forecast period, reaching a valuation of US$ 1.8 billion by 2027.
In the ever-evolving realm of construction, the fusion of innovation and tradition has given rise to a transformative trend - the integration of fibers into concrete. This article explores the remarkable journey of fiber-infused construction solutions, a paradigm shift that is reshaping the way we build by reinforcing concrete with newfound strength, durability, and versatility.
The Evolution of Fiber-Infused Concrete:
Traditional concrete has long been the backbone of construction, admired for its compressive strength but challenged by factors like cracking and tensile weakness. Enter fiber-infused concrete, a revolutionary approach that addresses these limitations by incorporating various types of fibers into the mix. This innovation introduces a new level of structural integrity, making concrete more resilient and adaptive to the demands of contemporary construction projects.
Types of Fibers Transforming Concrete:
Steel Fibers: Renowned for their high tensile strength, steel fibers are adept at reinforcing concrete against cracking and increasing its ductility. This type of fiber is particularly effective in enhancing the performance of industrial floors and precast elements.
Polypropylene Fibers: Lightweight and resistant to chemicals, polypropylene fibers contribute to concrete's ability to resist shrinkage cracks. They are commonly used in applications where corrosion resistance and impact strength are essential.
Glass Fibers: Offering a unique blend of tensile strength and corrosion resistance, glass fibers are versatile in applications where electrical conductivity is a concern. They are frequently employed in architectural and decorative concrete.
Synthetic Fibers: Various synthetic fibers, including nylon and polyester, are employed to enhance the toughness of concrete. These fibers improve resistance to impact, abrasion, and freeze-thaw cycles, making them suitable for a range of applications.
Key Advantages of Fiber-Infused Concrete:
Crack Control: One of the primary benefits of fiber-infused concrete is its ability to control cracking. The fibers act as micro-reinforcements, limiting the development of cracks and improving the overall durability of the structure.
Increased Durability: The addition of fibers enhances the durability of concrete, making it more resistant to the effects of weathering, chemical exposure, and other environmental factors. This results in longer-lasting structures with reduced maintenance needs.
Enhanced Flexural Strength: Fiber-infused concrete exhibits improved flexural strength, making it more capable of withstanding bending and tension forces. This is particularly valuable in applications such as bridges and pavements.
Versatility in Applications: Fiber-infused concrete's versatility extends its applications to a wide range of construction projects, including residential buildings, commercial structures, industrial facilities, and infrastructure projects.
The Future of Fiber-Infused Construction:
As the construction industry continues to embrace sustainability, efficiency, and resilience, the rise of fiber-infused construction solutions is set to become even more pronounced. Continued research and development in fiber technology, along with advancements in manufacturing processes, will contribute to the widespread adoption of this innovative approach.
Conclusion:
The reinvention of concrete through fiber-infused construction solutions marks a pivotal moment in the construction industry's evolution. As builders, architects, and engineers increasingly recognize the transformative potential of fiber-reinforced concrete, we witness the birth of structures that not only stand the test of time but redefine the possibilities of what can be achieved in the realm of construction. The rise of fiber-infused construction solutions is more than an innovation; it's a bold step towards building a more resilient, sustainable, and adaptable future.