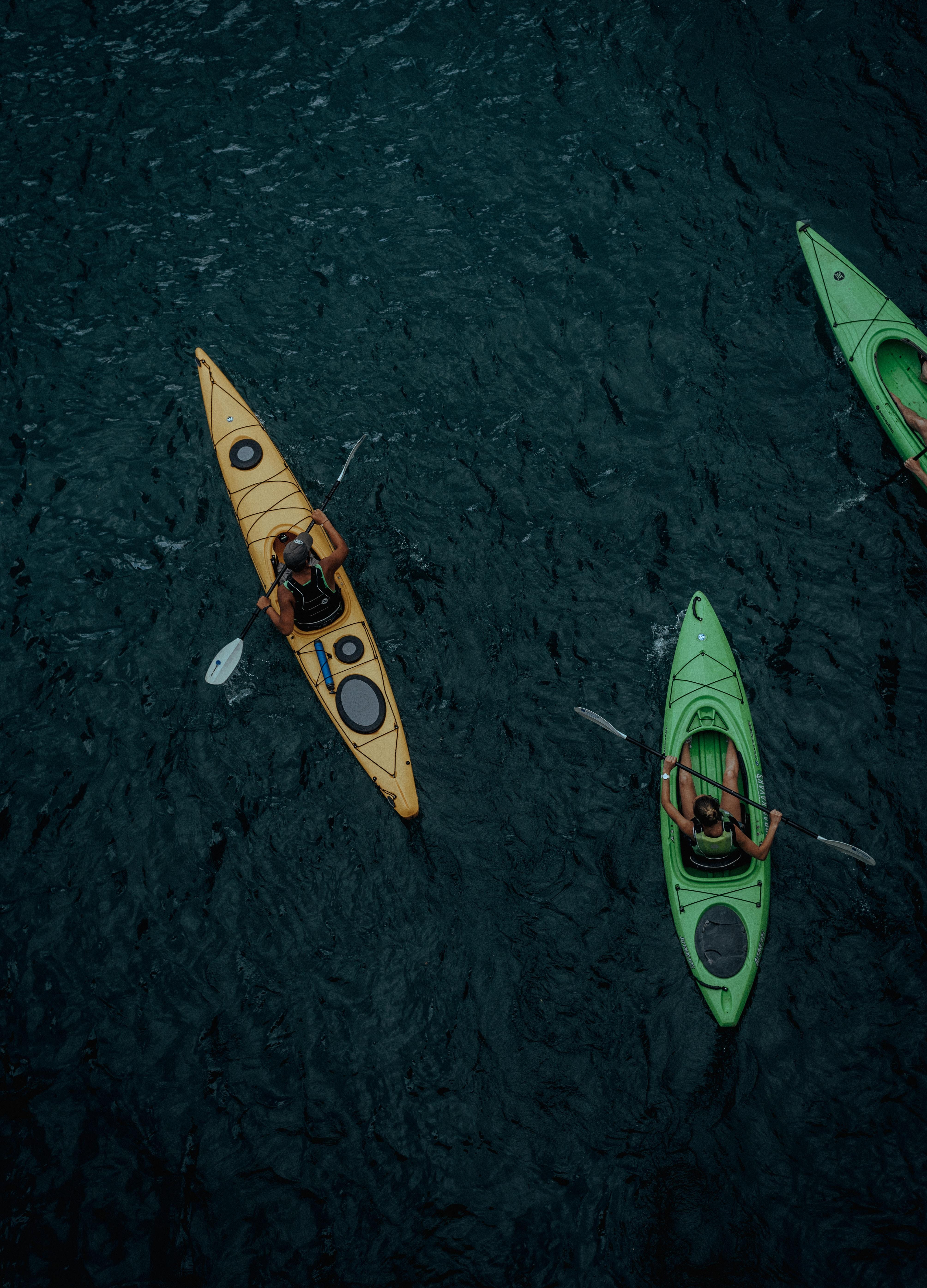
Kayaking is one of the water sports that require a paddler to face the direction of the dinghy, using a paddle with no fixed fulcrum, and using muscle strength to paddle backward. The sport is a sport that combines competition, entertainment, viewing, and adventure and is loved by everyone. Canoeing is played by athletes in a defined course and is based on speed. Modern canoeing has become one of the most popular sports in coastal countries and regions in the world, and it is also an important part of sports and cultural exchanges among people of all countries. Regular kayaking can strengthen physical fitness and exercise will.
The origin of kayaking
Canoeing is a sporting event that is divided into two sports: kayaking and rowing. Kayaking is divided into still water and whitewater events. Competitions held on natural or artificial lakes are called still-water events. Races in fast-flowing rivers are called whitewater events.
For thousands of years, due to the development of production and social progress, canoes have been replaced by other boats. However, in some remote areas, canoes still have their unique vitality, such as in the Samoan archipelago in the South Pacific, the Hida people of Colombia, who still manufacture and use canoes to this day, and also organize civil canoe races.
Modern canoeing - kayaking began in 1865, McGregor rowed around France, Germany, Sweden, and other European countries from 1865~1867, compiled the book "Norbu, Noi A Thousand Miles", and actively promoted kayaking. In 1867, he founded the Royal Canoe Club of England, which held its first canoe competition.
The sport of kayaking is on the rise
At the end of the 19th century, kayaking became a widely practiced sports activity in Europe and the United States. During this period, many people were enthusiastic about the transformation of the boat shape to increase the speed of the boat. German engineers made the kayak into a fish shape and increased the speed of the boat. British boat builder Fronte found that the longer the hull, the less resistance and the faster the speed, so shipbuilders lengthened the hull. In 1923, the working committee stipulated that the length of the boat was 5.2m and the width was 51cm, which has been used to this day.